For a long time, the total amount of potential safety hazards of scaffolds ranks among the top three
. 
For example, the scaffold erection and acceptance are not standardized, the daily maintenance and inspection are not in place, and the operators work on the scaffold with defects, which will bring great personal injury safety risk to the operators on site, especially the problems of high row scaffold and bearing frame, which will easily cause mass casualties and production safety Accident; through the detailed analysis and carding of on-site scaffold safety hazards, sort out the types of hidden dangers in the erection and use of 20 common types of scaffolds on site, and attach the corresponding standard requirements and rectification comparison photos, for the reference and learning of all participants on site, improve the safety skills of all staff to identify scaffold safety hazards
. 
This paper can also be used by construction units in the safety disclosure and training of on-site scaffold erection and acceptance personnel, to remind them to pay attention to the following violations in the process of scaffold erection and acceptance, to ensure that the on-site scaffold is erected and accepted according to the specification requirements, and do daily inspection and maintenance according to the requirements, so as to ensure the safety of on-site operators
. 
1
. 
Hidden danger of scaffold without sweeping pole: incomplete frame structure, individual pole instability, affecting the overall stability
. 
× lack of vertical and horizontal sweeping poles for scaffolds √ relevant standards for adding vertical and horizontal sweeping poles (article 6.3.2 of jgj130-2011) require that vertical and horizontal sweeping poles must be set for scaffolds
. 
The longitudinal sweeping pole shall be fixed on the vertical pole not more than 200 mm away from the bottom of the steel pipe with right angle fasteners
.
The horizontal sweeping pole shall be fixed on the vertical pole close to the bottom of the longitudinal sweeping pole with right angle fastener
.
2
.
Hidden danger of scaffold pole hanging: it is easy to cause instability of scaffold body, uneven stress and collapse
.
× the vertical pole of the scaffold is suspended and not on the ground √ the relevant standard for laying the base plate at the bottom of the vertical pole (article 8.2.3 of jgj130-2011) requires: during the use of the scaffold
.
The foundation shall be free from water, the base shall be free from looseness, and the vertical pole shall be free from suspension
.
3
.
Hidden danger of longitudinal horizontal bar and vertical bar butt joint in synchronization or in the same span: causing local uneven stress of scaffold and affecting stability
.
The requirements of relevant standards (article 6.3.6 of jgj130-2011) are as follows: two adjacent longitudinal horizontal bar joints shall not be set in synchronization or the same span; the staggering distance of two adjacent joints in water direction of asynchronous or different spans shall not be less than 500mm; the distance from each joint center to the nearest main node shall not be greater than 500mm 1 / 3 of the distance (article 6.2.1 of jgj130-2011); the joints of two adjacent vertical poles shall not be set in synchronization, and the staggered distance of two adjacent joints separated by a vertical pole in the synchronous direction shall not be less than 500mm; the distance between the center of each joint and the nearest main node shall not be greater than 1 / 3 of the step distance
.
4
.
The installation of wall connecting parts is not standardized, and the hidden danger is to reduce the anti overturning ability of scaffold
.
× the top layer of scaffold is lack of wall connecting parts √ the relevant standard of adding wall connecting parts (article 6.4 of jgj130-2011) requires: it should be arranged close to the main node, and the distance away from the main node should not be more than 300 mm; it should be arranged from the first longitudinal horizontal bar of the bottom layer; the wall connecting parts should be set horizontally, when it cannot be set horizontally, it should be connected downward to one end of the scaffold; the two ends of the open scaffold must be set The vertical spacing of wall connecting parts shall not be greater than the floor height of the building, and shall not be greater than 4m; the double row scaffold with a height of more than 24m shall be connected with the building by rigid wall connecting parts; the layout spacing of wall connecting parts can generally be arranged as three steps and three spans, two steps and three spans, etc
.
5
.
Hidden danger of lack of cross bracing or nonstandard erection: the overall rigidity of scaffold becomes low and the longitudinal stability decreases
.
X lack of cross bracing on the outside of the frame √ set up cross bracing according to the relevant standards (article 6.6.3 of jgj130-2011): the width of each cross bracing should not be less than 4 spans, and should not be less than 6m
.
For double row scaffolds with inclination angle between 45 ° and 60 ° and height of 24m and above, cross bracing shall be set continuously on the facade of outer ring; for single row and double row scaffolds with height of 24m and below, cross bracing shall be set on the facade of outer end, corner and middle interval of not more than 15m respectively, and shall be set continuously from bottom to top
.
6
.
Hidden danger of lack of transverse diagonal bracing or nonstandard erection: lack of triangular stability of diagonal bracing and decrease of frame stability
.
X scaffold is lack of transverse diagonal bracing √ relevant standard of adding transverse diagonal bracing (article 6.6.4 of jgj130-2011) requires: the transverse diagonal bracing of double row scaffold shall be arranged in the same section in zigzag form from the bottom layer; for double row scaffold with height below 24m, transverse diagonal bracing is not required; for closed scaffold with height above 24m, transverse diagonal bracing shall be set at every 6 spans except corner The two ends of the open double row scaffold must be provided with transverse diagonal braces
.
7
.
The scaffold is not fixed with fasteners or the torsion moment does not meet the requirements
.
Hidden danger: the scaffold steel pipe has no stable connection, which easily leads to the frame deformation
.
X the fastener is loose or the tightening torque does not meet the specification requirements √ re fix the fastener and meet the requirements of relevant standards (article 7.3.11 of jgj130-2011): the steel pipe shall be connected with fastener, and the bolt torsion torque shall not be less than 40n · m, and shall not be greater than 65N · M
.
8
.
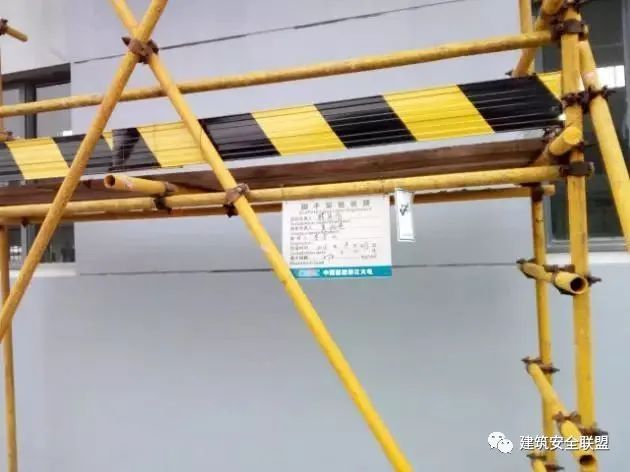
The lack of protective railings on the working platform or passageway is a potential hazard: people are prone to fall during walking or operation
.
X there are no protective railings on both sides of the passageway and no safety belt hanging points √ relevant standards for protective railings (article 6.7.2, 7.3.12 of jgj130-2011) are added
.
The requirements are as follows: protective railings shall be set on both sides of the ramp and both sides of the platform
.
The protective railings shall be composed of upper and lower cross bars and balustrades
.
The height of the upper bar from the ground is 1.2m and that of the lower bar is 0.6m
.
9
.
Lack of toe boards on both sides of the ramp and platform, hidden danger: it is easy to cause the risk of falling objects to hurt people
.
× there is no toe board on both sides of the passage with people passing below √ the relevant standard for setting toe board (article 6.7.2 of jgj130-2011) requires that toe boards should be set on both sides of the ramp and on both sides of the platform, and the height of the toe board should not be less than 180mm
.
10
.
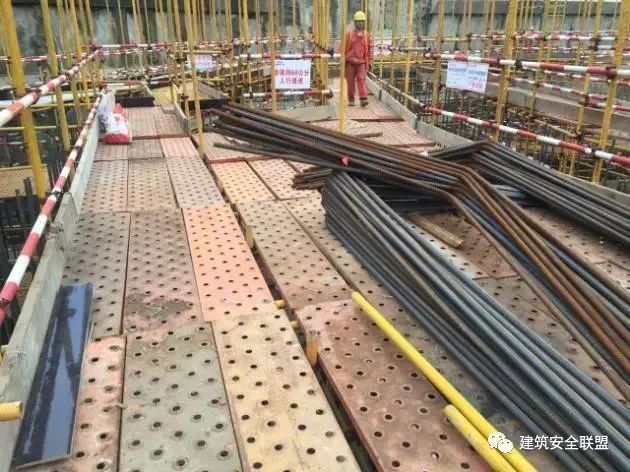
The scaffold board is not laid in a standard way and is not fully laid according to the requirements
.
Hidden danger: it is easy to cause people to fall and fall objects to hurt people
.
The scaffold board shall be fully paved according to the requirements of relevant standards (article 6.2.4 of jgj130-2011): the scaffold board of operation layer shall be fully paved; the scaffold board shall be laid by overlap or butt joint; when the scaffold board is laid by butt joint, two horizontal bars shall be set at the joint, and the extension length of scaffold board shall be 130-150 mm
.
The total extension length of two scaffold boards shall not be greater than 300 mm; when the scaffold boards are overlapped and laid, the joint shall be supported on the horizontal bar, the overlapping length shall not be less than 200 mm, and the length extending out of the horizontal bar shall not be less than 100 mm; both ends of the scaffold board shall be bound and fixed
.
11
.
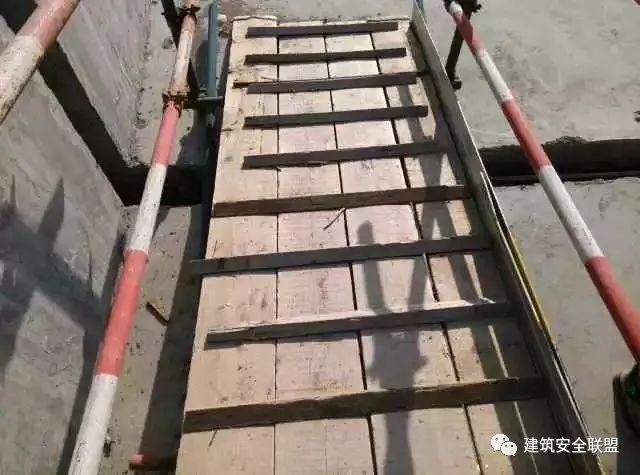
Hidden danger of too large slope of scaffold ramp: operators are easy to slip and get injured during walking
.
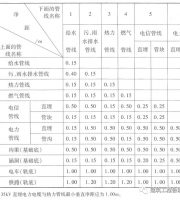
According to the relevant standard (article 6.7.2 of jgj130-2011), the width of the material conveying ramp shall not be less than 1.5m, and the slope shall not be greater than 1:6; the width of the pedestrian ramp shall not be less than 1m, and the slope shall not be greater than 1:3
.
Hidden danger: the steel pipe is easy to loose and slide out, and the scaffold is unstable.
.