1.9 Each unit shall register the hazard sources, among which the major hazard sources and the general hazard sources with major risk level shall establish special files to clarify the responsible department and person in charge of management.

11) This guideline is applicable to the identification and risk assessment of hazard sources in the construction of water conservancy and hydropower projects.
1.5 Legal person of water conservancy construction project and units participating in survey, design, construction and supervision (hereinafter referred to as each unit) It is the main body of hazard identification, risk assessment and control.

2.3 The risk level of hazard sources is divided into four levels, from high to low, followed by major risk, major risk, general risk and low risk.
1.8 During the construction period, each unit shall implement dynamic management of hazard sources, timely grasp the hazard sources and risk status and change trend, update the hazard sources and risk level in real time, and formulate targeted prevention and control measures according to the hazard sources and risk status.
1.6 The identification of hazard sources and risk level evaluation are divided into two stages: before the commencement of the project and during the construction period.
2.1.4 operating environment: unfavorable geological sections, potential landslide areas, over standard flood, dust, toxic and harmful gas and toxic chemical leakage environment, etc.
3 Hazard identification 3.1 Hazard identification refers to the process of analyzing hazard factors, identifying the existence of hazard sources and determining their characteristics, including identifying hazard sources and determining their characteristics Hazard category and level.
3.2 For hazard identification, professionals with rich experience and familiar with engineering safety technology shall use scientific, effective and applicable methods to identify the hazard sources of the project, classify and classify them, summarize and formulate the list of hazard sources, and determine the name, category, level, possible accident type and responsible person of hazard sources.
2.1.5 other categories: field construction, fire safety, camp site selection, etc.
3) and The guidelines are formulated in the opinions of the office of the safety committee of the State Council on implementing the guidelines for curbing major and major accidents and building a dual prevention mechanism (AWB [2016] No.
Major hazard sources in the construction of water conservancy and hydropower projects (hereinafter referred to as major hazard sources) It refers to the parts, areas, places, spaces, posts, equipment and their locations that have potential energy and substance release hazards during the construction of water conservancy and hydropower projects, may lead to personnel death, serious health damage, serious property loss and serious environmental damage, and can be transformed into accidents under the action of certain triggering factors.
for new technologies adopted for the first time , new process, new equipment, new materials and single projects with high risk without relevant technical standards shall be identified and risk evaluated as hazard source objects.
1.3 Construction hazard sources of water conservancy and hydropower projects (hereinafter referred to as hazard sources) It refers to the position, area, place, space, post, equipment and location where there is potential energy and material release danger during the construction of water conservancy and hydropower projects, which can cause casualties, health damage, property loss and environmental damage, and can be transformed into accidents under the action of certain trigger factors.

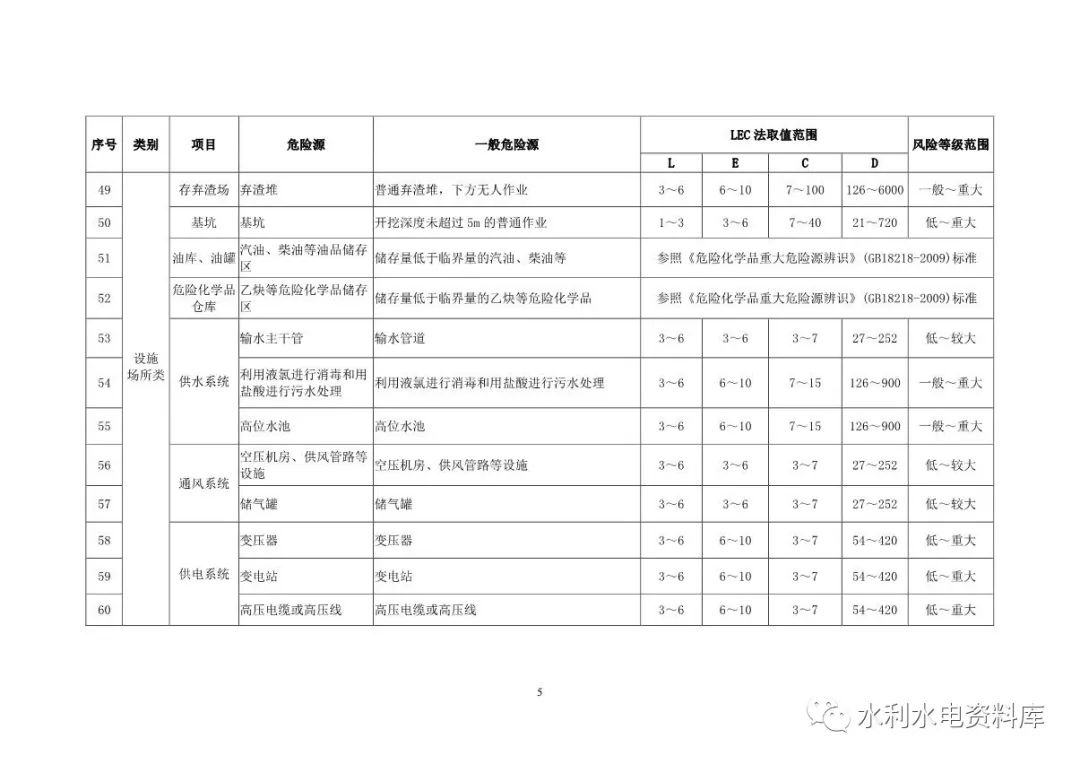
2.1.3 facilities and places: slag storage yard, foundation pit, blasting equipment warehouse, oil depot, oil tank farm, material and equipment warehouse, water supply system, ventilation system, power supply system, repair plant, reinforcement plant and mould Processing plant and other metal structure fabrication and processing plant sites, prefabricated component sites, construction roads, bridges, tunnels, cofferdams, etc.
2.1.2 mechanical equipment: transportation vehicles, special equipment, hoisting, installation and disassembly, etc.
1.7 Before commencement, the project legal person shall organize other participating units to study and formulate hazard identification and risk management system, and clarify the responsibilities, identification scope, processes and methods of supervision, construction and design units; the construction unit shall organize hazard identification and risk level evaluation of this bid section as required, and submit the results to the project legal person and the supervision unit in time; the project legal person shall Carry out hazard identification and risk level assessment of the project, and prepare hazard identification and risk assessment report.

2.2 There are two levels of hazard sources, namely major hazard sources and general hazard sources.
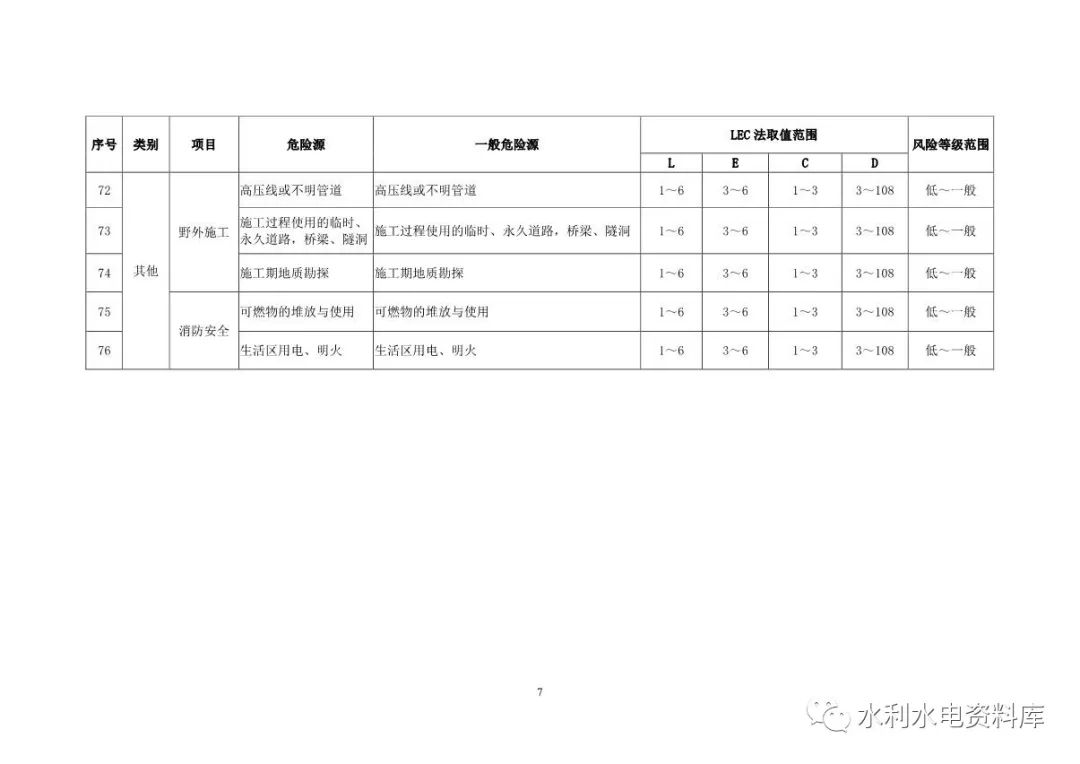
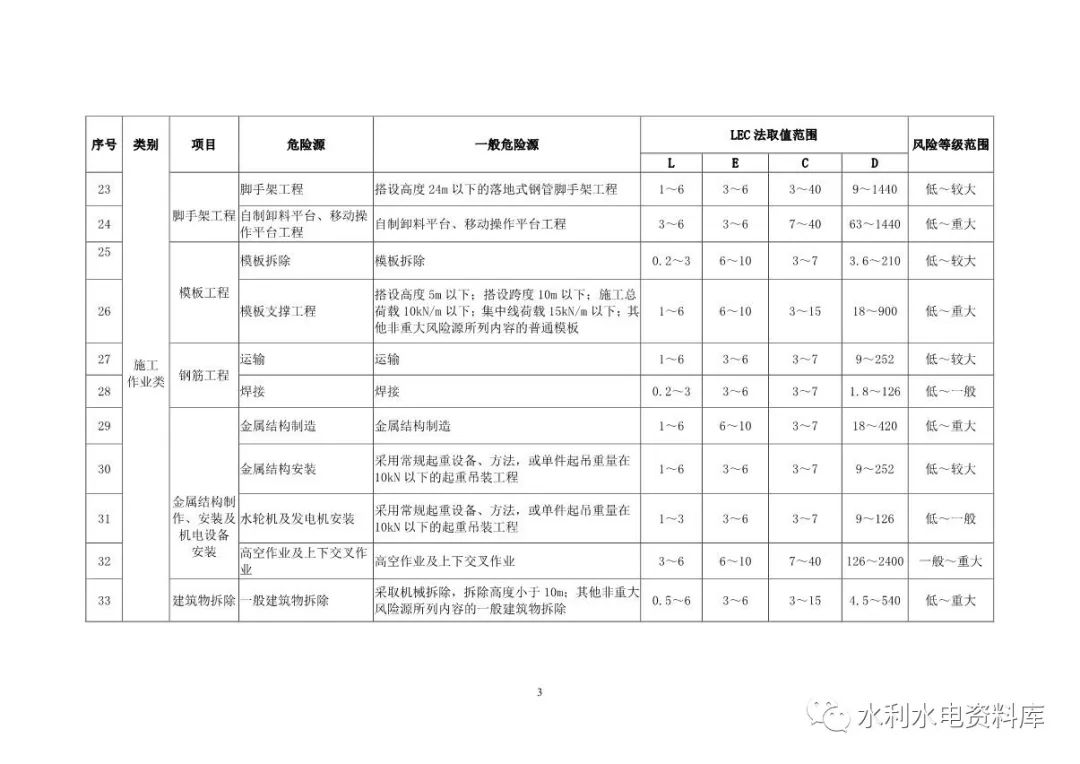
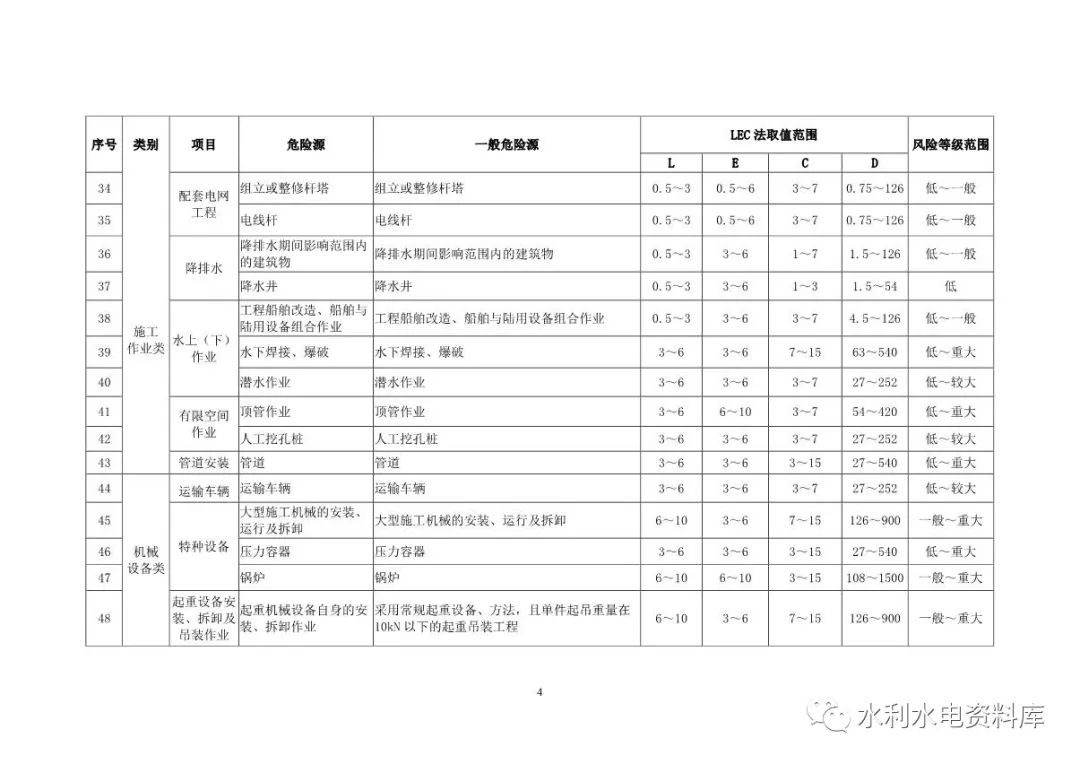
The identification and evaluation objects of various types mainly include: 2.1.1 construction operation: open excavation construction, tunnel excavation construction, rock blasting, filling engineering, grouting engineering, inclined shaft and shaft excavation, geological defect treatment, sand and stone production, concrete production and concrete Pouring, scaffold engineering, formwork engineering and support system, reinforcement fabrication and installation, metal structure fabrication and installation and electromechanical equipment installation, building demolition, supporting power grid engineering, dewatering and drainage, above (below) water Operation, confined space operation, high-altitude operation, pipeline installation, other single works, etc.
For the production, storage, use and transportation of dangerous goods in the project area, the hazard source identification and risk assessment shall refer to relevant national and industrial laws, regulations and technical standards Hazard identification and risk assessment shall strictly comply with relevant national and water conservancy laws and regulations, technical standards and these guidelines.
The hazard identification and risk assessment report shall be signed and confirmed by the person in charge and the main person in charge of the work safety management department of the unit, and experts shall be organized for review and confirmation if necessary.
2.3.4 low risk: the probability of risk events and the degree of harm are small; mild hazards are under the control of the construction unit.
See Annex 1 for main contents and requirements.
If necessary, collective discussion or expert technology can be carried out Demonstration.
Major hazard sources include the safety production law Defined major hazard sources of dangerous goods.
2.3.3 general risks: the probability of occurrence of risk events is medium, and the degree of harm is small; medium risks are controlled by the construction unit and supervised by the supervision unit Supervisor.
Guidelines for hazard identification and risk assessment of water conservancy and Hydropower Engineering Construction one total Then 1.1 In order to scientifically identify and evaluate the construction hazard sources and risk levels of water conservancy and hydropower projects and effectively prevent construction and production safety accidents, according to the work safety law of the people’s Republic of China, the notice of the office of the safety committee of the State Council on printing and distributing the work guidelines for tackling both the symptoms and root causes and curbing major and extraordinarily serious accidents (Anwei ban [2016] No.
two Hazard source category, level and risk level 2.1 Hazard sources are divided into five categories: construction operation, mechanical equipment, facilities, working environment and others.

2.3.2 major risks: the probability of occurrence of risk events and the degree of harm are medium, or the degree of harm is medium, and the probability of occurrence of risk events is small; high risks are jointly controlled by the construction unit organized by the supervision unit and supervised by the project legal person.
2.3.1 major risk: the probability of risk event and the degree of harm are large, or the degree of harm is large and the probability of risk event is medium; extremely dangerous risks are jointly controlled by the supervision unit and the construction unit organized by the project legal person and supervised by the competent department Inspection.
The major hazard sources shall be reported to the project competent department and relevant departments for the record according to relevant regulations.1.10 Each unit can appropriately supplement the content of hazard sources in accordance with relevant laws, regulations and technical standards, combined with the actual situation of the unit and the project, and determine the risk according to the method of this standard.
The water administrative department and river basin management organization shall, in accordance with relevant laws, regulations and technical regulations The standard and this guideline provide guidance, supervision and inspection for hazard identification and risk assessment.
All units shall comprehensively carry out hazard identification and risk assessment, strictly implement relevant management responsibilities and control measures, and effectively prevent and reduce safety production accidents in accordance with the actual situation of the project and the conditions and management characteristics of the project construction site.
3.3 Direct judgment method, safety checklist method, pre hazard analysis method and causal analysis method can be adopted for hazard identification..




