④ The loss and waste of cement should be avoided and environmental protection should be done well.
④ Continuous grading or discontinuous grading is determined by experiments.
Including water reducing agent, air entraining agent and pumping agent.
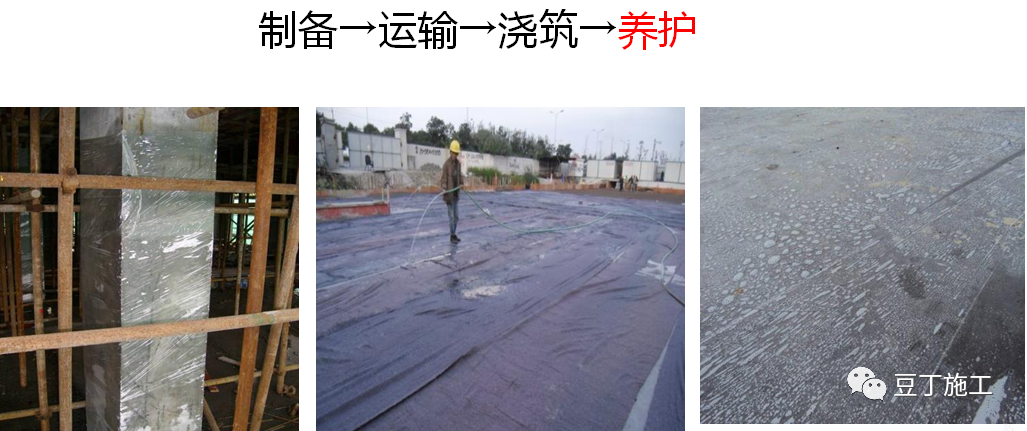
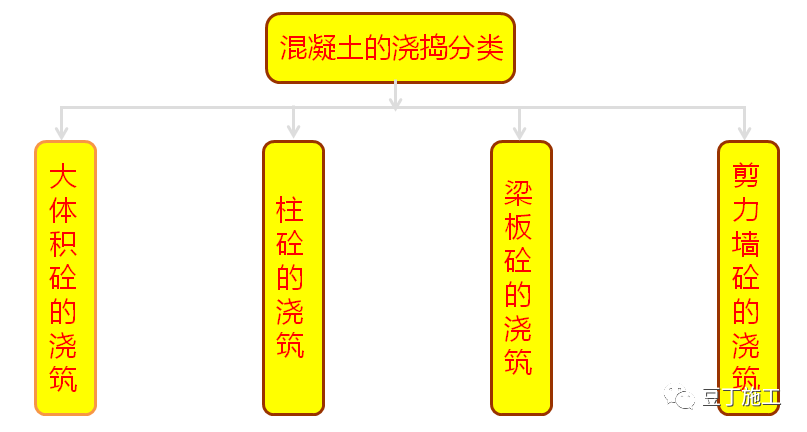
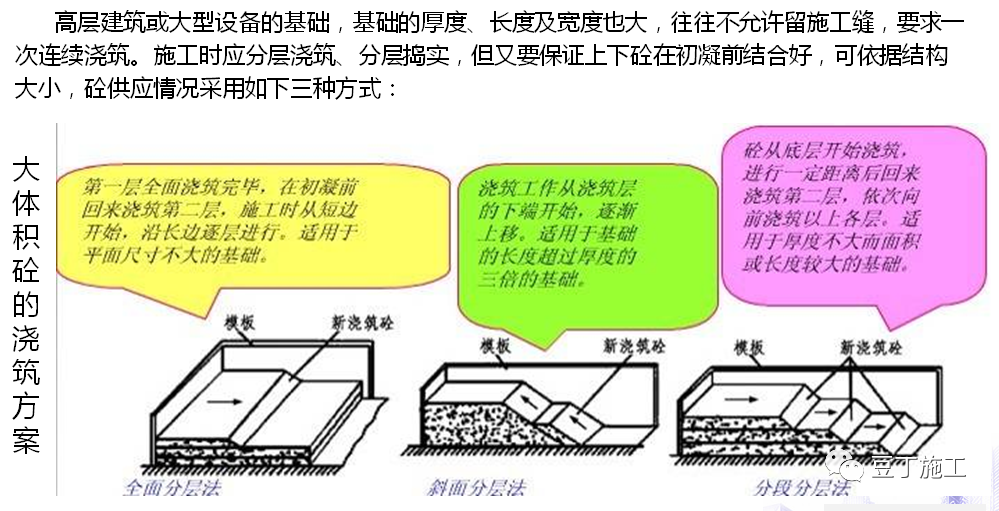
quality control of concrete pouring 3.1 introduction to quality control points of concrete pouring (1) sundries in the formwork or on the cushion shall be removed before concrete pouring..
1.2.2 classification and application control of aggregate (1) quality requirements of coarse aggregate: ① the maximum particle size of coarse aggregate shall not exceed two-thirds of the clear distance of reinforcement, one-quarter of the minimum side length of component section and one-half of the thickness of plain concrete slab.

1、 Concrete raw materials 1.1 introduction to concrete raw materials 1.1.1 water: all drinking water can be used for mixing and curing concrete.


③ The grading content of aggregates at all levels shall be controlled.
It is not allowed to contain oils, sugars or other harmful impurities that affect the normal setting and hardening of cement, and the pH value is not less than 4; The sulfate content is not more than 1%.
Admixtures to improve the durability of concrete.


⑤ The surface of coarse aggregate shall be clean, and any powder, mud or contamination shall be removed.
It is divided into coarse aggregate and fine aggregate.
① Misuse of mix proportion; ② During concrete batching, the measurement of any material is out of control or missing; ③ Uneven mixing or entrainment of raw materials; ④ the slump of outlet concrete exceeds the maximum allowable range.

D.
2、 Concrete mixing control 2.1 concrete mixing ratio 2.2 concrete mixing quality control key points of concrete mixing quality control: (1) minimum mixing time of concrete.
Including air entraining agent, waterproof agent and rust inhibitor.

C.
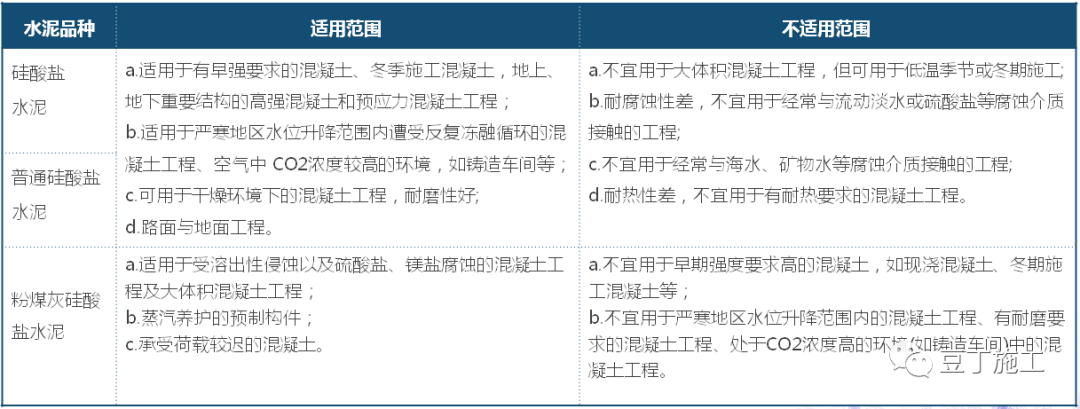
1.1.2 cement: there are many kinds of cement, which are divided into general cement, special cement and special cement according to their use and performance.
The quality requirements of aggregate include: strength, frost resistance, chemical composition, particle shape, grading and impurity content.
admixtures that improve the rheological properties of concrete mixtures.
1.2.4 special role of fly ash in concrete fly ash is the fine ash collected from the flue gas after coal combustion.
② The cement transported to the mixing plant shall be stored in the warehouse with obvious marks according to the indicated variety, strength grade, manufacturer and ex factory batch number, and shall not be mixed.
The use of mountain sand, coarse sand and ultra-fine sand should be demonstrated by experiments.
The main oxides are SiO2, Al2O3, FeO, Fe2O3, Cao, TiO2, MgO, K2O, Na2O, SO3, MnO2, etc., in addition to P2O5, etc.

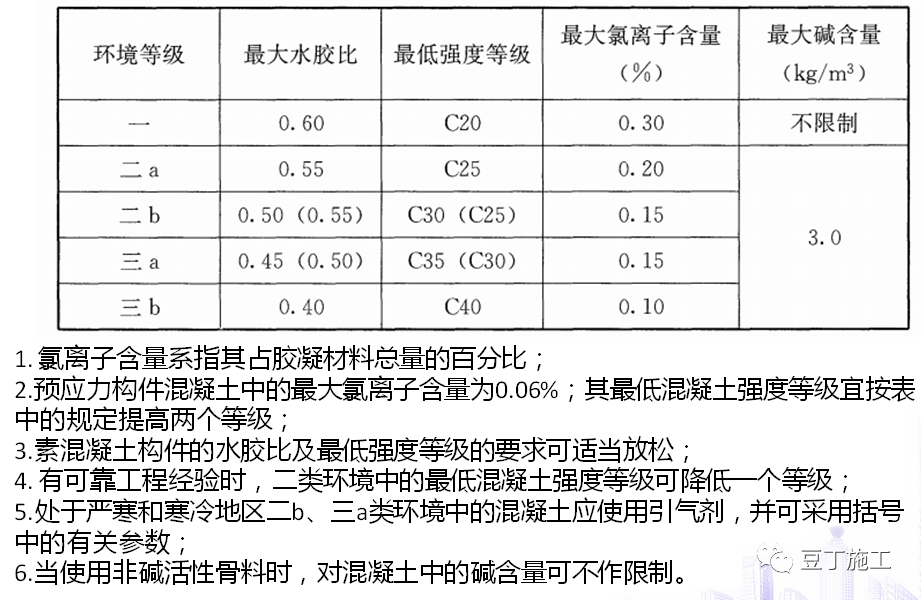
According to jgj52-2006 standard for quality and inspection methods of sand and stone for ordinary concrete (with article description): the limit value of mud content in sand varies according to the strength grade of concrete: 1.
It shall be determined according to the mixing capacity, maximum aggregate particle size, mixing method, etc.
Solid Lifting Socket Cross Pin
Untreated industrial wastewater, sewage and marsh water cannot be used, and seawater is not allowed for reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete projects.
Including aerating agent, expansion agent, antifreeze, colorant, waterproof agent and pumping agent.
2.3 precautions for concrete transportation III.
2.
The mud content in sand greater than or equal to C30 concrete is ≤ 3.0%; Less than C30, silt content ≤ 5.0%.
For concrete sand with frost resistance, impermeability or other special requirements, the silt content shall not be greater than 3.0%.
Including retarder, early strength agent and accelerator.
Concrete admixtures are divided into the following four categories according to their main functions: A.
③ See relevant standards for other quality requirements, such as mud content, mud lump content, firmness, sulfide and sulfate content, organic matter, apparent density, mica, light matter, stone powder content, etc.
General cement is divided into Portland cement, ordinary portland cement, fly ash Portland cement, slag Portland cement, pozzolanic Portland cement and composite Portland cement: 1.1.3 aggregate: sandstone aggregate is the most basic component of concrete.
Fly ash is the main solid waste discharged from coal-fired power plants.
1.2.3 classification and application control of admixtures: admixtures are substances added in the process of mixing concrete to improve the performance of concrete, and the amount of admixtures is not more than 5% of the quality of cement (except for special circumstances).
General cement is mainly used in general civil engineering projects.
⑥ When there is doubt about the quality of cement in use or the cement leaves the factory for more than three months (fast hardening portland cement for more than one month), retest shall be carried out, and the cement can be used again only after passing the retest.
When the particle size is 80mm, it is divided into three levels D20, D40 and D80; When the particle size is 150 (120) mm, it is divided into four levels: D20, D40, D80 and D150 (D120).
(2) Quality requirements for fine aggregate: ① fine aggregate shall be hard, clean and well graded; The fineness modulus of artificial sand should be in the range of 2.4 ~ 2.8, and that of natural sand should be in the range of 2.2 ~ 3.0.
1.2 application and control of concrete raw materials 1.2.1 application and control of cement: the following points should also be paid attention to in the construction process: ① give priority to the use of bulk cement.
Admixtures to adjust the setting time and hardening performance of concrete.
For concrete structures with little or no reinforcement, larger coarse aggregate particle size should be selected.
② During the construction, the coarse aggregate is divided into the following particle size combinations according to the particle size: when the particle size is 40mm.
(2) The moisture content of aggregate shall be regularly detected during concrete mixing.
B.
It is divided into two levels D20 and D40.
Additives to improve other properties of concrete.
If necessary, accelerated dehydration measures shall be taken.
③ Cement shall be waterproof and moisture-proof during transportation and storage, and cement that has been caked by moisture is not allowed to be used.

⑥ See relevant standards for other quality requirements, such as mud content, mud lump content, firmness, sulfide and sulfate content, organic matter content, apparent density, water absorption, needle and flake particle content, etc.
(3) In case of any of the following conditions, the concrete mixture shall be treated as unqualified.

② The moisture content of fine aggregate shall be kept stable, and the moisture content of saturated surface of artificial sand shall not exceed 6%.