[Construction Specification] coarse aggregate above 4.75mm for the base course of extremely heavy and extra heavy traffic load grade of Expressway and class I highway shall be of single particle size.
In addition, the uneven road surface will also accumulate rainwater and accelerate the damage of the road surface.
Therefore, it is required to minimize dust on the road during driving.
The compactness test during construction shall be based on the maximum dry density determined by the compaction results sampled on site every day.
2、 The subgrade width of class III and IV highways is generally composed of lanes and shoulders, as shown in Figure 1-2.
If the strength or deformation resistance of the whole or a part of the subgrade and pavement structure is insufficient, the pavement will have diseases such as fracture, settlement, wave or rutting, which will affect the normal use of the subgrade and pavement.
With sufficient surface anti sliding performance, the pavement surface shall be flat, but not smooth.
The materials used for building the surface course mainly include cement concrete, asphalt concrete, asphalt crushed (gravel) stone, gravel (gravel) mixture with soil (or without soil), block material, etc.
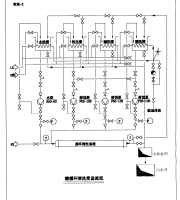
2、 Pavement structure level the pavement structure is usually paved in layers, that is, it is divided into several levels according to the use requirements, stress conditions, soil foundation support conditions and the influence degree of natural factors.
See table 1-2 for material type and application scope of pavement surface course.
The stability of pavement structure with sufficient stability means that the pavement structure can better maintain the geometric shape, physical and mechanical properties required by engineering design under the action of natural factors such as water and temperature.
Subgrade is a geotechnical structure excavated or filled on the natural ground surface according to the requirements of the design linearity (location) and design cross section (geometric dimension) of the route.
In order to improve the durability of pavement, in addition to careful design, selection of materials and fine construction, it is also very necessary to maintain, repair and restore road performance frequently and in time.
The base course and subbase base course mainly bear the vertical force of vehicle load transmitted from the surface course and diffuse the force to the underlying cushion and soil foundation.
With the lowest dust emission, the vacuum suction generated behind the vehicle body will suck out the fine particles on the road surface and cause dust, resulting in looseness, falling off and pit damage on the road surface.
The skid resistance of asphalt pavement surface is usually realized by hard, wear-resistant and rough surface coarse aggregate, while some technological measures (such as grooving) will be taken for cement concrete pavement.
When driving at high speed in rainy days, when emergency braking or sudden starting, climbing or turning, the wheels are easy to spin or slip, resulting in a decrease in driving speed, an increase in fuel consumption, and even traffic accidents.
The flatness shall be accepted for Subgrade handover acceptance, and the flatness shall be accepted for all structural levels of pavement.
The roadbed is divided into two layers: upper roadbed (0 ~ 0.3m) and lower roadbed (0.3 ~ 0.8m).
The subgrade width of Expressway and class I highway is generally composed of lane, median and shoulder, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Roadbed: the roadbed within 0.8m below the bottom of the pavement structure layer is called roadbed.
Lower Embankment: the filling part below the upper embankment is called lower embankment.
This kind of vibration will cause driving bumps and affect the speed and safety of driving, the stability of driving and the comfort of passengers.
In the cold and freezing season in the north, asphalt pavement, cement concrete pavement and semi-rigid base will produce a large number of shrinkage cracks due to low temperature.
Pavement is a layered structure paved with various mixtures for vehicles on the top of subgrade.
It is the foundation of the pavement and bears the driving load transmitted from the pavement.
1、 The basic structure of pavement subgrade and pavement are the main engineering structures of highway.
The surface layer is a structural layer that directly bears the repeated action of wheel load and the influence of natural factors.
The uneven road surface will increase the driving resistance and cause additional vibration to the vehicle.
B if the difference between this value and the maximum dry density determined in the design stage is greater than 0.02g/cm3, the cause shall be analyzed and handled in time.
When the base course is too thick, it can be divided into two or three layers to ensure the project quality.
When the car runs on a smooth road, there is a lack of sufficient adhesion (friction) between the wheels and the road.
Under the repeated action of wheel load, it is easy to produce cracks or break plates.
Therefore, the surface layer should have high structural strength, deformation resistance, good water stability and temperature stability, and should be wear-resistant and impermeable; The surface shall also have good skid resistance and flatness.
During the handover and acceptance of subgrade and pavement, generally, the bearing capacity of flexible materials (such as graded crushed stone and asphalt concrete) is expressed by deflection, and the bearing capacity of rigid materials (such as cement concrete) and semi-rigid materials (such as inorganic binder stabilized materials) is expressed by strength.
The pavement structure with sufficient durability will age and decay under the repeated action of driving load and cold, hot and dry and wet climate factors, and the service performance of the pavement will gradually reduce, resulting in fatigue damage and plastic deformation accumulation, so as to shorten the service life of the pavement.
The compaction test sampled every day shall comply with the following provisions: a the compaction test shall not be less than 3 parallel tests, and the difference of maximum dry density between them shall not be greater than 0.02g/cm3; Otherwise, the test shall be repeated, and the average value shall be taken as the detection standard of compactness on that day.
Excellent pavement flatness shall be ensured by excellent construction equipment, fine construction technology, strict construction quality control and regular and timely maintenance.
According to the different functions of each layer, the pavement structure layer can generally be divided into surface layer, base layer, subbase and cushion, as shown in Figure 1-3.
Due to softening of asphalt pavement in high temperature season, large deformation will occur under the action of wheel load.
The stability of pavement structure mainly includes overall stability, water stability, temperature stability (high temperature stability or low temperature stability), etc.
[Construction Specification] sufficient thickness shall be ensured for mixture paving.
With sufficient surface flatness, pavement surface flatness is an important performance affecting driving safety, driving comfort and transportation benefits.
When the subbase is double-layer, it can be called upper subbase and lower subbase respectively..
Therefore, the pavement structure must have sufficient fatigue strength, resistance to aging and resistance to cumulative deformation, so as to maintain or prolong the service life of the pavement.
1、 The vehicle with sufficient bearing capacity running on the highway transmits the vertical force, horizontal force, vibration force and impact force generated by the vehicle to the pavement through the wheels, resulting in stress, strain and displacement in the pavement structure.
When different materials are used to build the base course, the lower layer is the subbase.
Upper Embankment: the filling part 0.8 ~ 1.5m below the bottom of the pavement structure layer is called upper embankment.
The periodic change of air temperature has an important impact on the stability of pavement structure.
Road dust will affect the driving sight distance, reduce the driving speed and bring adverse effects on the environmental sanitation along the line.
When substandard lime is used for roads below class II, the effective calcium oxide content shall be more than 20%, and the strength of the mixture shall meet the requirements.
[Construction Specification] the lime of Expressway and class I highway shall not be lower than class II, that of class II highway shall not be lower than Class III, and that of highway below class II shall not be lower than class III.
After rolling and forming, the paving thickness of each layer shall not be less than 160 mm, and the maximum thickness shall not be greater than 200 mm.
At the same time, it is also affected by rain erosion and temperature change.
Ground hydrated lime should be used for the base course of Expressway and class I highway.
It bears the vertical force, horizontal force and impact force of large driving load.
The cement concrete pavement panel will warp and deform in high temperature season.